Direct trade is a model of international trade that involves the direct purchase of goods and products from small-scale producers and farmers, bypassing traditional intermediaries such as importers, wholesalers, and distributors. This approach to trade has the potential to create a range of positive impacts on local economies and communities around the world.
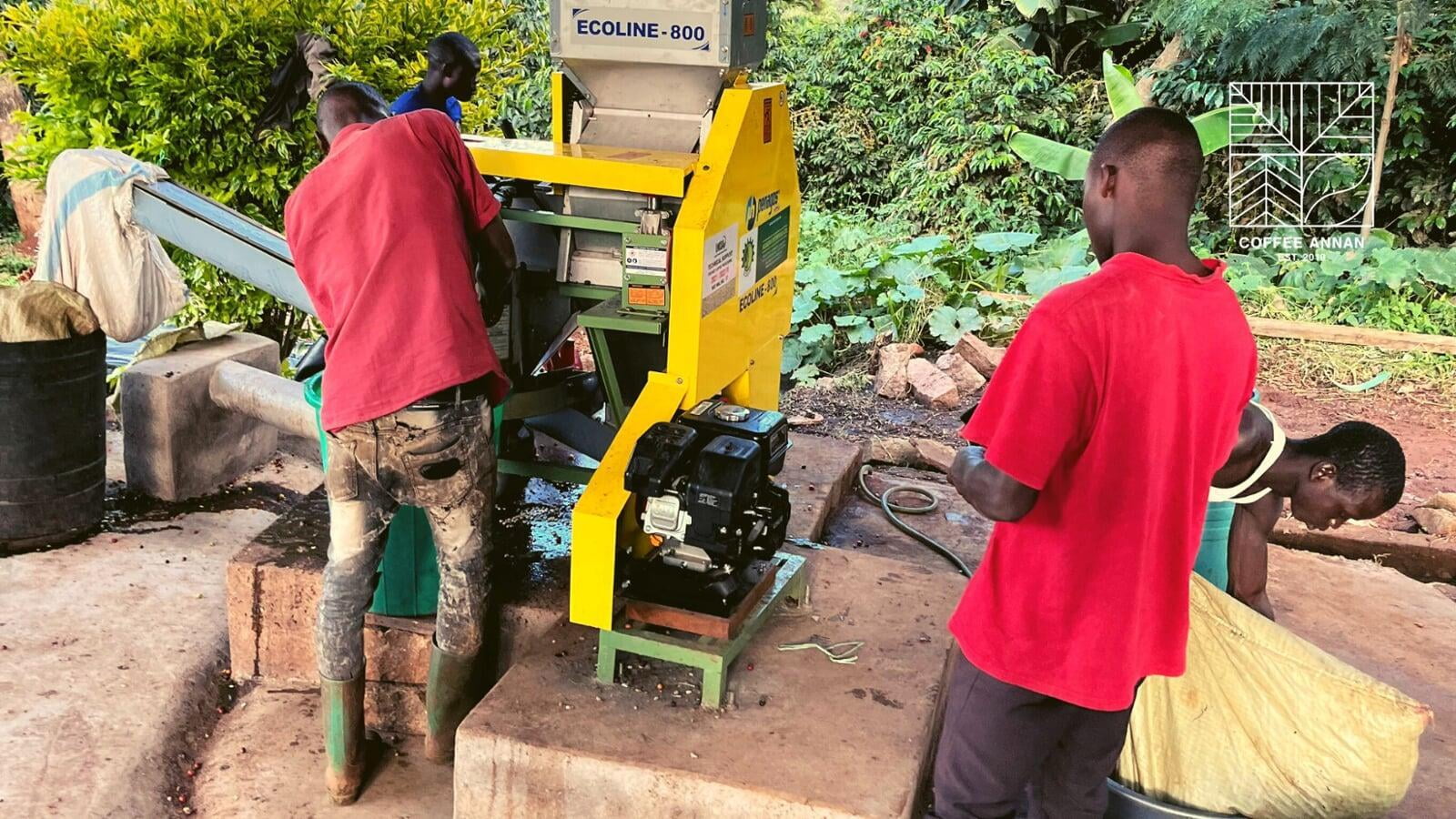

One key benefit of direct trade is the ability to support small-scale producers and farmers. These producers often struggle to access global markets due to a lack of resources and connections, and as a result, they may be forced to sell their goods at low prices to intermediaries. Direct trade offers an alternative by allowing producers to sell their products directly to buyers, often at higher prices and with better terms. This can provide a much-needed source of income and stability for producers, helping to lift them out of poverty and improving their standard of living.
In addition to supporting small producers, direct trade can also have a positive impact on local economies. When producers are able to sell their products directly, they are more likely to reinvest their profits in their communities, supporting local businesses and creating jobs. This can lead to the development of strong, sustainable local economies that are less reliant on external sources of income and support.

Direct trade can also contribute to the cultural preservation of communities. Many small-scale producers are involved in traditional crafts and techniques that are unique to their regions and cultures. By supporting these producers through direct trade, buyers can help to preserve these traditions and skills, ensuring that they are passed down to future generations.
Another potential benefit of direct trade is its ability to promote fair labor practices and working conditions. When producers are able to sell their products directly, they are more likely to have control over the prices they receive and the terms of their work. This can help to ensure that workers are paid fairly and treated ethically, as they are not reliant on intermediaries who may cut corners in order to maximize profits.
While direct trade has the potential to create a range of positive impacts, it is not without its challenges and limitations. One key issue is the need for buyers to have a strong understanding of the conditions and needs of the producers they are working with. This requires a significant investment of time and resources in building relationships and gathering information. It also requires buyers to have a willingness to pay fair prices for products, which may be higher than those offered by intermediaries.
Another limitation of direct trade is that it may not be suitable for all types of products or producers. Some producers may not have the capacity to meet the demand of large buyers, or may not have the resources to engage in direct trade. In these cases, intermediaries may be necessary to facilitate trade.

Despite these challenges, there are many examples of successful direct trade programs that have had a positive impact on local economies and communities around the world. One such example is the coffee industry, where direct trade has become increasingly popular in recent years. Many small-scale coffee producers in developing countries struggle to access global markets and receive fair prices for their products. Direct trade offers an alternative by allowing producers to sell their coffee directly to buyers, often at higher prices and with better terms. This has helped to support the livelihoods of small producers and contributed to the development of strong, sustainable local economies.
One of the key advantages of direct trade is the opportunity it provides for buyers and producers to develop long-term, mutually beneficial relationships. These relationships can be based on trust, transparency, and a shared commitment to sustainability and social impact. By working directly with producers, buyers can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities faced by these communities, and can work together to find creative solutions.
For example, direct trade can help to support producers in improving the quality of their products and increasing their efficiency. This can involve providing access to training and resources, such as new technologies or marketing assistance. By investing in the growth and development of producers, buyers can help to create more sustainable and successful businesses, which can in turn benefit local economies and communities.
In addition to the benefits outlined above, direct trade can also contribute to a more transparent and accountable global supply chain. By working directly with producers, buyers can have a greater understanding of the conditions and practices involved in the production of their products. This can help to ensure that products are produced ethically and sustainably, and that producers are treated fairly.
There are many ways that consumers can support direct trade and contribute to its positive impacts on local economies and communities. One simple way is to choose products that are labeled as "direct trade", which can help to support small-scale producers and promote ethical and sustainable practices. Consumers can also research the supply chains of the products they buy, and look for companies that are committed to direct trade and social responsibility.
Another way to support direct trade is to advocate for it within the broader community. This can involve sharing information about the benefits of direct trade with friends and family, and supporting businesses and organizations that promote it. Consumers can also advocate for policy changes that support small-scale producers and promote fair and sustainable trade practices.
In conclusion, direct trade has the potential to create a range of positive impacts on local economies and communities around the world. By supporting small-scale producers and farmers, promoting fair labor practices and working conditions, and contributing to cultural preservation, direct trade can help to create a more just and sustainable global economy. While there are challenges and limitations to direct trade, there are also many success stories and examples of companies that have implemented successful direct trade programs. By supporting direct trade and advocating for it, consumers can play a role in creating a more positive and equitable future for all.
